Functional binders to tackle transition metal dissolution in LNMO cathode material
Le Thuy Truong
SINTEF Industry
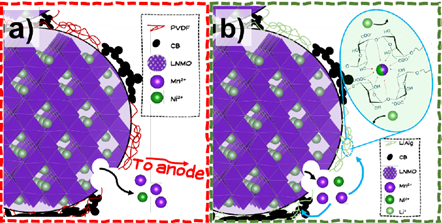
LNMO is a promising cathode material for high-energy Li-ion batteries. To fully utilize LNMO cathodes, there are challenges to solve. One of them is the oxidation of carbonate electrolytes, which in the presence of water generates HF that leads to the dissolution of transition metal ions. These dissolved ions then migrate to the anode where they are reduced to metallic form, causing increased resistance and capacity degradation over time. The H-EU project IntelLiGent focuses on developing non-fluorinated binders for LNMO cathodes with metal-ion scavengers to mitigate the issue of TM dissolution, thus trapping harmful parasitic species before they reach the anode. Various binders have been investigated, including lithiated versions of alginates with different Mw, polyacrylic acid and HPAM at varying pHs, where the electrochemical cycling shows a dependence on the binders’ functionality based on both Mw and pH levels. Methods to prove and quantify TM uptake will be discussed.